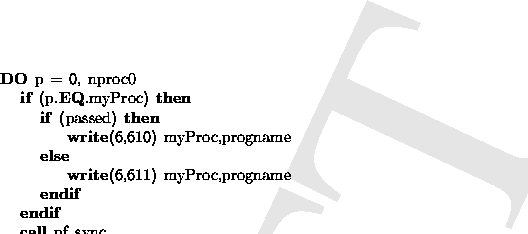


Next: 4 Test Program Descriptions
Up: Testing
Previous: Testing
Subsections
We have written a number of test programs for
the Planguage translators, pfc and pcc.
These tests must execute correctly for a satisfactory
install. Software designers may also benefit from
studying these programs.
In section 3.1 we describe the requirements
for adding a test to the Planguage test suite. The codes
themselves are overviewed in section 4.
The parallel Pfortran and PC tests reside in the
directories plang/pf/tests and plang/pc/tests, respectively.
Pfortran tests have a .PF suffix, and
PCtests have .PC suffix.
A test becomes an active component of the automated
testing system when it is a member of the test
directory makefile macro PLANGTESTS,
and the Planguage source code is in the respective
test directory.
Planguage tests must meet certain requirements
so to function in the automated test environment.
The areas, which are described below, are:
- 1.
- output
- 2.
- reserved variables and labels
- 3.
- default variables
The general output from a test program can be anything, with
the exception that, to standard output (stdout),
the keyword passed occuring on the
same line with the test program name have special meaning;
see section 3.2 on reporting success for details.
Automated test output is sent to any of four places:
- file plang/tmp/test.out: stdout (cleared after
each program executes).
- file plang/tmp/test.llog: running record of all stdout
- file plang/tmp/test.log: pass/fail information
- file tty: pass/fail information
The following variable names and labels are reserved words
for report.fh (see below): passed,
p, progname, and labels 610 and 611.
While these names are commonly used, the reservation only applies
to the test programs in the Planguage suite.
The following default names must be used for
- myProc for the local process,
- nProc for the number of processes,
- nProc0 for the zero-based number of processes.
A test is successful if the program ran
without encountering any problems at any process.
Test analysis relies on the test program outputting pass
and fail information to stdout (the analysis script
automatically routed to test.out).
A successful test is reported as follows:
For a passed test,
report outputs to stdout and the file
plang/tmp/test.log the string
<process number> passed test <program name>
and for failed tests, the string
<process number> passed test <program name>.
To facilitate
this, the test program should use the include
file report.fh (report.h) in the tests directory
for Pfortran (PC). The Pfortran include
file report.fh follows.
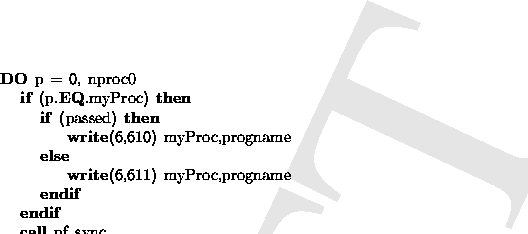
Thus, the following definitions must be made in the test program
- logical: passed defined true if all tests succeeded;
otherwise defined as false if any test failed,
- character string: progname defined as the program name.
The Planguage execution and processing of the test cases
is performed by the Perl script runtests.pl
in the tests directory.
The tests require these environment variables,
which are used in the Planguage build system:
- PLANG_MPROCS: the maximum number of processes,
- PLANG_PLATFORM: the operating system and machine,
- PLANG_NETINT: the network interface,
- PLANG_TOP: the root of the Planguage distribution.
Subsequent to building the test programs and defining the
environment variables, one makes test in the test
directory. This is automatically performed with
a Planguage install.
Process configuration starts from two processes
up thru PLANG_MPROCS in step increments defined in
runtests.pl.



Next: 4 Test Program Descriptions
Up: Testing
Previous: Testing
Terry Clark
8/2/1998